Dry Conditions Increasing BMSB Movement Into Tree Fruit. Adult Threshold Exceeded in Mid-Hudson Valley. September 16th, 2024
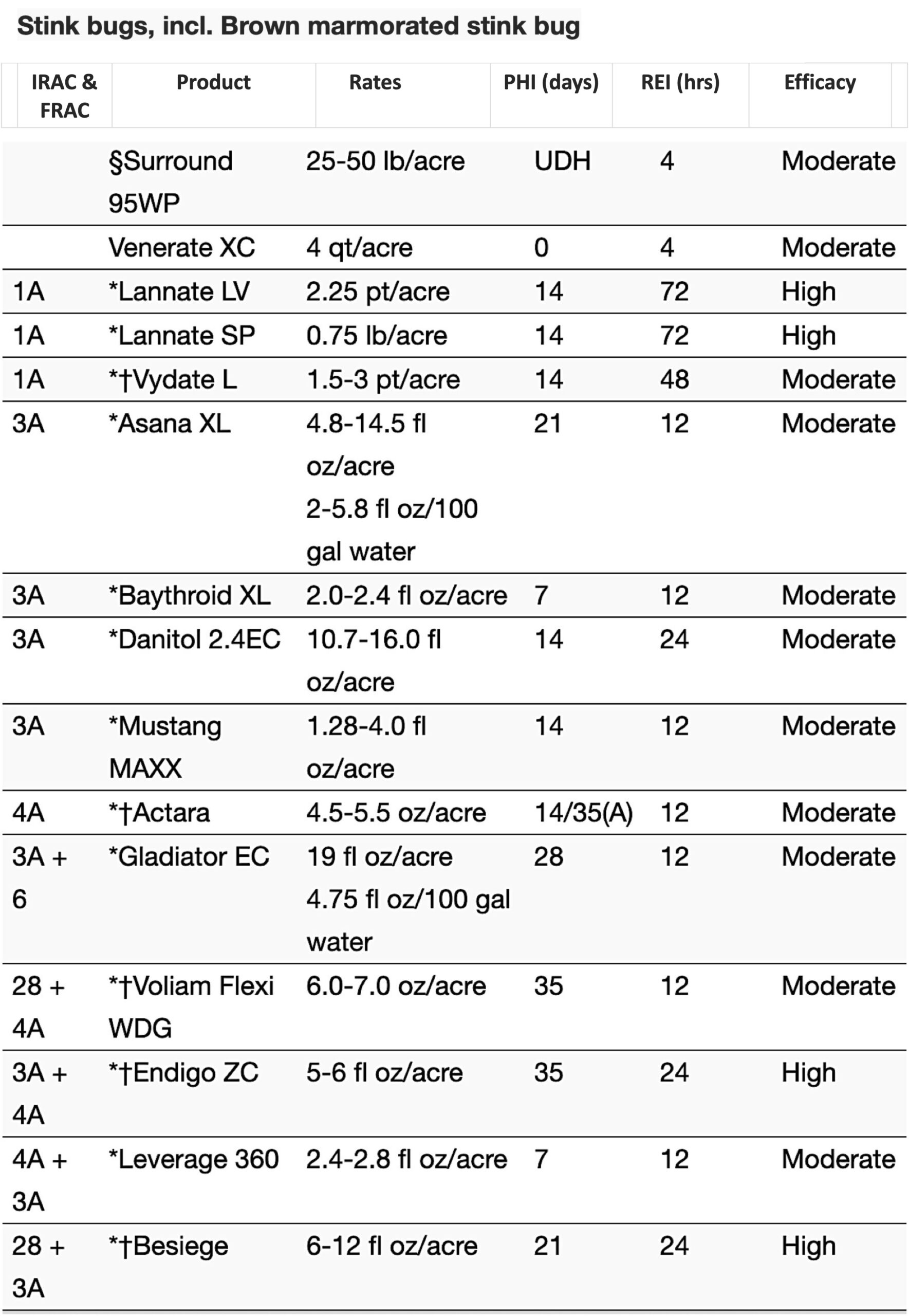
Synopsis: 1st and 2nd generation adult Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha halys (BMSB) are increasing, nearing or exceeding threshold throughout Orange and Ulster County. Overwintering adults are now highly attracted to the ‘aggregation’ pheromone, making their way into homes and traps, and increasing in numbers throughout mid-Hudson Valley orchard sites this past week. Very dry conditions prevail, increasing the risk of BMSB infestation to orchard fruit as BMSB seeks moisture from irrigated fruit.
Movement of the insect to apple foliage and fruit and fruit feeding is continuing in untreated orchards with damage to fruit observed. Trap numbers of stink bug in combination with scouting for the insect in perimeter tree canopy should precede management during this time of BMSB population build-up. Review labels for pre-harvest intervals (PHI) when choosing materials as the most effective materials have 14 DTH constraints.
When thresholds are exceeded or stink bug become visible along the orchard edge, border row applications should begin. These should then be followed by alternate row, then whole orchard applications as movement of native and BMSB populations begin to migrate into orchards.
As stink bug are orchard edge opportunists, the majority of the injury to fruit will occur along the wooded orchard edge, 30′ to 90′ along the perimeter into the block of varieties highly susceptible. These include Golden & Red Delicious, Empire, Ruby Frost, EverCrisp and the last standing…Pink Lady. As fruit diminishes through harvest, BSMB funnel to the remaining fruit, which could be heavily injury in October through early November.
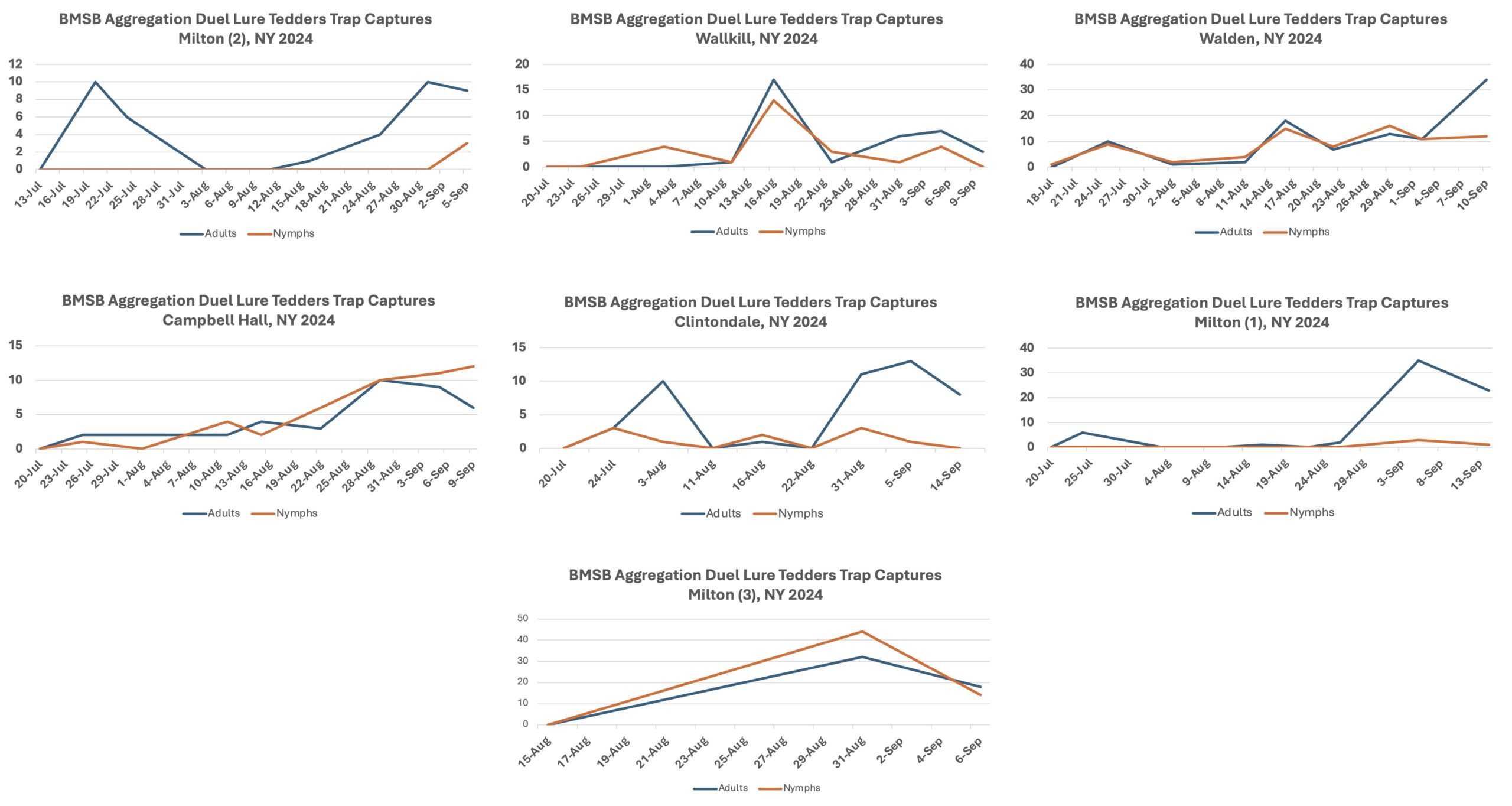
BMSB Trap Captures in Mid-Hudson Valley using Tedders Traps and duel pheromone lures along commercial orchard perimeter woodland locations.
Scouting including duel aggregation pheromone trap observations are important to determine insect presence along the orchard perimeter a 10 adult BMSB Tedders trap per week or captures of 2-3 BMSB on ‘baited’ sticky card on post indicates pest presence requiring orchard management.
Perimeter and alternate row applications (ARM) beginning at threshold may suffice under low population levels. As the insect is quite mobile through flight and crawling, its movement through the canopy will increase its contact with insecticide residue under ARM.
Overview:
The brown marmorated and native green stink bug are arboreal insects, residing in woodland habitat and feeding primarily on seed bearing trees such as Tree of Heaven, Maple and over 300 other seed host plants they utilize for nourishment. However, when populations continue to rise through July into August, increasing numbers of adults and nymphs can be observed moving into tree fruit orchards. This will occur at higher levels if drought conditions occur. Increasing presence of the insects in trees will result in injury to late varieties of peach, pear and apple, predominately in rows bordering woodlands and hedgerows.
Nymphs and adults have been observed feeding on fruit along abandoned orchard perimeter trees this week. A partial second generation will significantly increase BMSB population in woodlands.
As host quality from the arboreal woodland habitat declines, increasing migration to tree fruit is very likely through the end of October. Increased scouting should be based on recent and upcoming Tedders trap captures. This will be especially important if weather turns dry with irrigated tree fruit becoming a favored host of BMSB as adults begin to feed more intensively as they prepare for their overwintering phase.
Monitoring: Remember that trap captures combined with scouting for the various life stages of the insect along the orchard perimeter rows should be the basis for insecticide applications. Unlike most other pests, we should not be using IPM thresholds based on stink bug feeding that results in fruit damage. SImply, the expression of the injury occurs 7-10 days or longer after feeding. As such, you would have missed your opportunity to reduced injury if you postpone preventative applications while waiting on injury that has already occurred to become visible.
Use a conservative presence and trap threshold on through harvest. Finding a single BMSB or green stink bug in the tree canopy within 100′ of scouted perimeter row would be considered a conservative threshold (no data to support this). Driving along the orchard will likely spook the insects. You’ll need to stealth your way quietly around the orchard…its good exercise in the early evening or early cool of the morning. Green stink bug tend to remain low in the canopy while BMSB tend to move to the tops of the trees to feed requiring us to scout the entire canopy.
Management: When BMSB populations dramatically increase during late season, migration into orchards can cause significant injury, predominately along the perimeter. BMSB have been known to funnel down to the last variety standing (such as the high value Pink Lady). In which case, applications in late October may be warranted!! Drought conditions also exacerbate BMSB injury as insects require more moisture, utilizing irrigated tree fruit.
When selecting insecticides for border row, alternate row and or whole orchard applications, you should consider constraints on your markets. If weather turns to drought, then longer residue based on the active ingredient minimum residue level (MRL) could become an issue, especially in EU and Israel markets. Review your options carefully with regards to harvest dates, PHI’s, re-application intervals and seasonal A.I. volume (Actara (Thiamethoxam).
One of the most effective tools for use to manage BMSB is the active ingredient bifenthrin in a number of formulations. Yet…Bifenthrin has a 12 hr. re-entry interval, 14 day pre-harvest interval and a 30 day re-application interval requiring rotational tools for effective management at 10-14d intervals and scheduling management for specific varieties based on the pre-harvest window. Danitol 2.4EC is one option for use during rotation with Brigade.
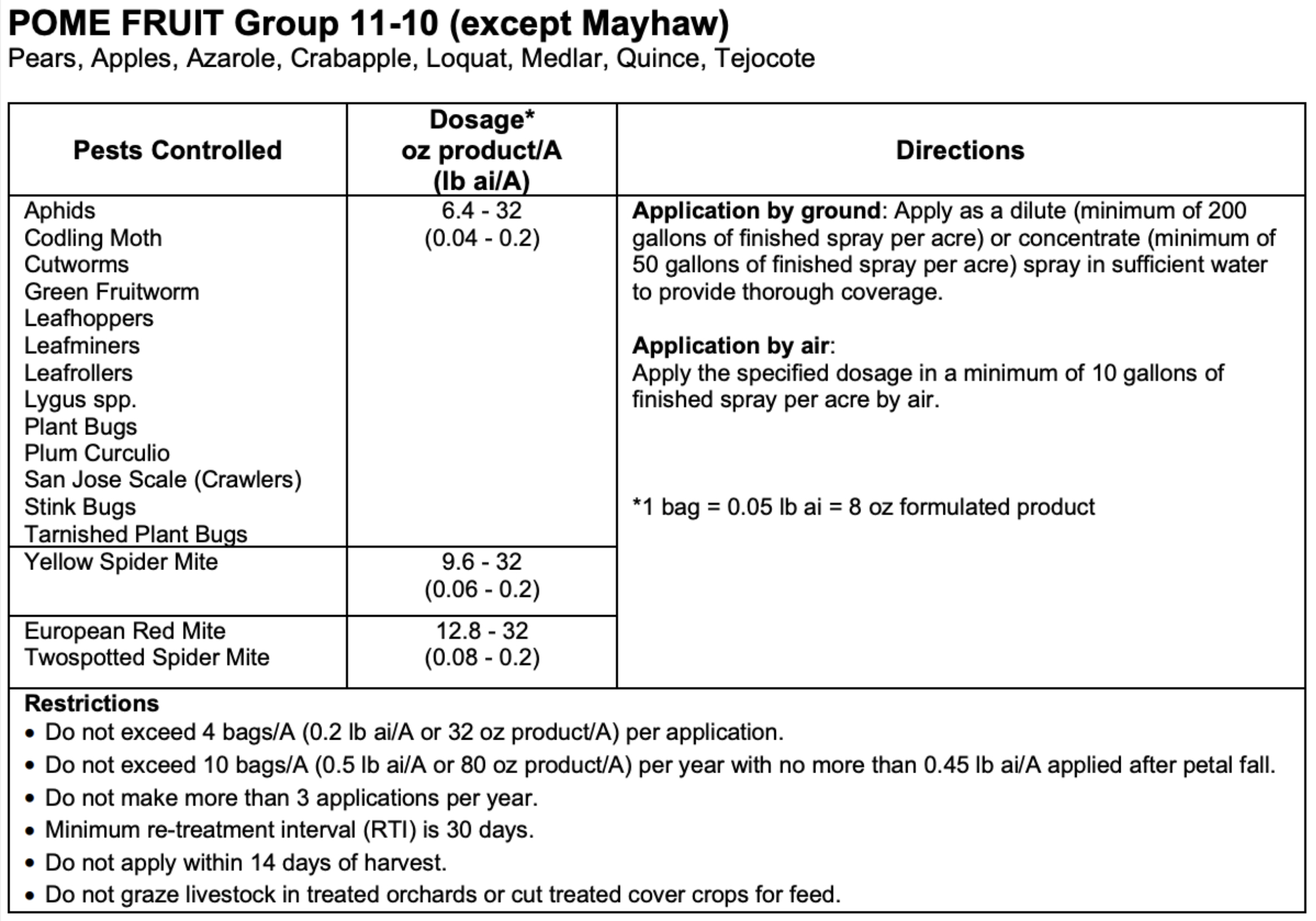
Brigade label application rates and restrictions for Pome Fruit.
Brigade WSB (Bifenthrin) is labeled for Pome Fruit in NYS. Do not apply more than a total of 0.45 lbs ai/acre per season post PF. Apply as necessary to maintain control using a minimum of 30‐day spray intervals, 14-day pre-harvest interval and a 12 hour REI.
Danitol 2.4EC is labeled for Pome Fruit in NYS and has a 12 hr. re-entry interval, 14 day pre-harvest interval and a 30 day re-application interval.
ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS FOR USE IN NEW YORK Do not apply this product within 100 feet of any freshwater lake, pond, river, stream or wetland in the state of New York. Do not apply this product within 100 feet of a coastal marsh or any water that drains into a coastal marsh in the state of New York. Aerial application is prohibited in the state of New York. Single application greater than 0.3 lb ai per acre and seasonal applications greater than 0.6 lb ai per acre are prohibited in the state of New York.
What to do up to 7 days to harvest: Leverage 360 has a 7-day pre-harvest window and has been shown to have excellent efficacy against BMSB from research trials across university studies.
What to do within 7 days to harvest: Keeping BMSB from feeding on the fruit is at the crux of our stink bug management program as we near harvest. Killing the insect as it moves into the orchard and onto the fruit is the traditional method of crop protection and proven to be very effective. Yet limitations, based on the material pre-harvest intervals constrain their use near harvest. There are no effective pyrethroids, neonicotinoids or pre-mixed insecticide tools that permit their use within the 7-day to harvest window with very few options available during the days prior to fruit harvest.
A Novel Mode of Action: The development of newer classes of insecticides that produce an anti-feeding response in the pest provides an additional mode of action for BMSB management. Corteva insecticide Closer 240 SC (classified as a Group 4C insecticide / neonicotinoid – 7 DTH) is available in the Northeast but not available in NYS. Yet Venerate XC (a microbial-based insecticide (ai. Burkholderia sp.) with multiple modes of action and O DTH) having anti-feeding activity against BMSB fruit feeding. The O DTH of Venerate provides BMSB management up to the day of harvest under high risk conditions (Data slides of efficacy trials).